Infrared Detector
Infrared detectors (also called infrared sensors or pyroelectric detectors) are optoelectronic components and represent the core element of gas analyzers, flame sensors, devices of spectral analysis, as well as non-contact temperature measurement. In DIN 1319-1, a detector is called a transducer, also known in Europe as a sensor, so that in the literature rather than referred to as an infrared detector, the terms infrared transducer and infrared sensor are often found.
InfraTec is specialized in the production of pyroelectric infrared detectors without cooling or temperature stabilization in a wide operating temperature range -55 ... 85 °C, capable of measuring the slightest amounts of infrared radiation (as little as a fraction of a nW) with wavelengths between 1 µm and > 25 µm. These infrared detectors are available in standardized housing types (TO18, TO46, TO5, TO39, TO8).
Principle of Infrared Radiation
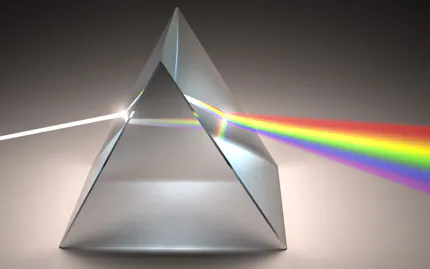
The principle of infrared radiation is based on the physical phenomenon that any body of a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15 °C) emits electromagnetic radiation. There is clear correlation between the surface of a body and the intensity and spectral composition of its emitted radiation. By determining its radiation intensity the temperature of an object can thereby be determined in a non-contact way.
Infrared radiation is that part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is immediately adjacent to the red light (infrared light) of approx. 760 nm on the long-wave side of the visible spectrum and extends to a wavelength of approx. 1 mm.
Advantages of Pyroelectric Infrared Detectors by InfraTec
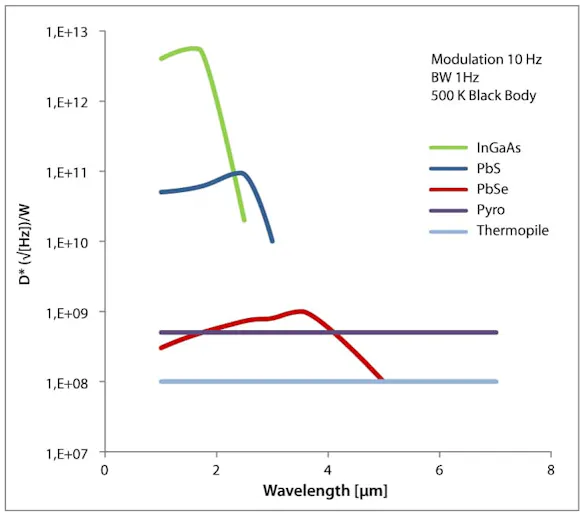
As part of the family of thermal detectors, a pyroelectric detector, unlike semiconductor detectors (InGaAs, PbS, PbSe), are equipped with a highly efficient, absorbent black layer and thus has an extremely broad, spectrally and laterally homogeneous sensitivity. Semiconductor detectors achieve a higher specific detectivity than pyroelectric infrared detectors when operated with up to a wavelength range of 3 µm at room temperature.
Compared to thermopile detectors, which may also detect long wavelength infrared radiation at room temperature, a pyroelectric infrared detector by InfraTec is much faster and operates with significantly higher signal voltage, even without additional preamplification. Optimal conditions for pyroelectric detectors are at wavelengths between 2.5 and 25 µm and modulation frequencies 0.5 to 400 Hz.
InfraTec pyroelectric infrared detectors use special black layers for absorption and can therefore even be used as large-scale, long-term stable receivers of UV radiation (i.e. 193 nm), but can also be used for THz radiation in the range of 100 µm to 1 mm.
Infrared Detectors Offer
High flexibility in terms of the measurement substances
Application chemometric methods for multi-component analysis
Measurement of known compositions with overlapping bands
Identification of unknown substances
Cost-effective, robust and miniaturized solution
The Infrared Detector in Use
The most common use of pyroelectric infrared detectors is for motion detection. Inexpensive pyroelectric ceramic sensors generally suffice for this purpose. Other applications include the non-dispersive infrared gas analysis (NDIR gas analysis) and infrared flame sensing and monitoring. In these areas, mainly high-quality, single-crystal lithium tantalate (LiTaO

Would You Like to Know More?
It is not unusual for tasks to be associated with special requirements. Discuss your specific application needs with our experienced engineers, receive further technical information or learn more about our additional services.
Manufacturing Excellence
All steps in development and production take place in our main building in Dresden, starting with development and simulation to design and prototyping to the volume production of detectors. Technologies are designed with redundancy and produce a complete in-house technological process. PVD, chip and wire bonding and product measurements are automated, what removes the variations of the manual manufacturing. This results in a constant high quality in all fields, even with the most demanding manufacturing and testing processes.
InfraTec pyroelectric infrared detectors use polished double sided LiTaO
Detector Search
InfraTec offers different product groups including approximately 50 standard pyroelectric detectors. Detectors with reduced microphone technology and integrated operational amplifier as well as digital detectors are part of our product range.
Choose your suitable infrared detectors with the help of our detailed detector search.